Many people do not always understand the difference between arthritis and osteoarthritis due to the similarity in names.Both diseases are associated with the joints, but the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and therefore treatment are fundamentally different.It is very important to determine the nature of the disease at the initial stage in order to begin appropriate treatment.
Arthritis, osteoarthritis and their effect on the joints.
To begin proper treatment of a joint, it is first necessary to determine what type of disease it is susceptible to.And for this it is necessary to understand for yourself what the difference is between arthritis and osteoarthritis.
Both diseases affect the joints, but have different symptoms and causes.
What is osteoarthritis?
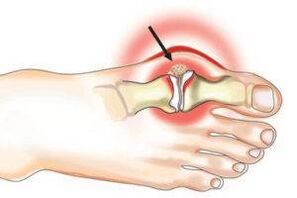
Osteoarthritis, sooner or later, affects approximately 10% of the population and manifests itself more frequently with age.Osteoarthritis is a deformation of the joints and a decrease in their mobility.Its correct name should be considered osteoarthritis.
The main symptoms are pain when moving and loss of mobility, the range of motion in the affected joint decreases, and an unpleasant, dry, sharp crunch appears when moving.Deformation can also be seen in osteoarthritis.For example, it is very easy to notice a change in the shape of the knee joint.
Osteoarthritis can be detected in the initial stage.The diagnosis is complicated only by the negligent attitude to health on the part of the patients themselves.Pain in the initial stage appears only with exertion, so many do not attach importance to it, which aggravates the disease and complicates treatment.
Arthritis and its symptoms.
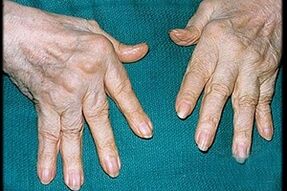
While osteoarthritis is a disease of the joints only, arthritis is usually infectious and affects the entire body.These diseases are one of the manifestations of the general condition of the body.It is much more difficult to treat, as well as to diagnose.Joint pain is accompanied by swelling and inflammation;The pain does not disappear, it only intensifies, much faster than in osteoarthritis.Infectious arthritis affects not only cartilage tissue, but also negatively affects the heart, kidneys and liver.Although arthritis is approximately 5 times less common than osteoarthritis, it is much more difficult to treat, it poses a great danger to the patient's life and its causes can be varied.
The main symptoms of arthritis are:
- high temperature;
- skin inflammation, psoriasis;
- general weakness of the body;
- discomfort in the eyes;
- discharge from the genitals;
- chills, increased sweating.
The skin around the joints is especially hot and swollen.
How does arthritis differ from osteoarthritis depending on the nature of the disease?
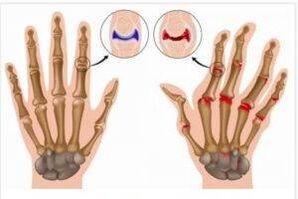
To better understand the causes of such diseases, it is necessary to understand their nature and classify them.
All joint diseases can be divided into two groups: inflammatory and dystrophic processes.
To determine the nature of a disease, the symptoms of which are similar to others, it is important to diagnose and determine the cause of a particular process in the body.
The main problem with both diseases is the imbalance in the joints between the destruction and repair processes.The stronger the imbalance, the faster the bone tissue is destroyed, which manifests itself at the cellular level in a lack of oxygen and nutrition for them, and in a poor production of healthy bone tissue components.
Most often, the process goes unnoticed and when the number of dead cells exceeds the norm, pain appears.Thus, the body tries to “complain” about excessive stress and asks for help.
Dystrophic diseases
Most often, these diseases have characteristic names that have the same endings: osteoarthritis, osteochondrosis, ligamentosis, osteoarthrosis.These diseases appear with age or with constant physical activity.Football players, for example, often suffer from osteoarthritis in the knee joint even at a young age.Most athletes are susceptible to knee joint diseases.
Joints have painful symptoms due to thinning of cartilage tissue, called degeneration.These diseases develop due to the general aging of the body, a sedentary lifestyle and the infectious nature of diseases that can accompany the development of osteoarthritis, osteochondrosis and similar diseases only accelerate the degeneration process.The body does not have time to replace dead cells, that is, to regenerate, and the reverse process occurs.The most difficult thing to stop is the widespread tissue degeneration of the knee joint.
inflammatory diseases
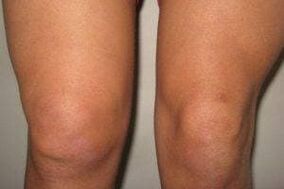
These diseases also have similar endings and often end in -it.Often infectious in nature, bacteria or viruses can cause inflammation of one or more joints, which will have corresponding symptoms:
- elevated temperature;
- swelling;
- perspiration
They can also be autoimmune or allergic-infectious in nature, when the body fights against its own cells.In this case, pain and swelling of the knee joint may indicate serious problems with the immune system.In case of pain in the knee or any joint, a doctor should be consulted immediately for a complete diagnosis of the body.
Often the cause of joint pain can be salt deposits in the cavities and periarticular tissues.In this case, there is a possibility of metabolic disorders.
Osteoarthritis and arthritis - treatment
Since the causes of the diseases are completely different (in osteoarthritis, the joint wears out mechanically, and arthritis is infectious), the treatment will be completely different.That is why it is so important to separate these two diseases.
Let's consider the treatment using the example of the knee joint.In both cases it is necessary to reduce the load as much as possible.Osteoarthritis of the knee joint or any other joint cannot be cured, since the process is irreversible.However, regular use of chondroprotectors can slow down the process, stimulate cartilage regeneration and reduce pain in the knee joint.
Infectious arthritis can be treated with antibiotics and medications that affect the immune system.In some cases, it will be necessary to repeat the treatment, but the disease itself is completely curable.
If the diagnosis showed rheumatoid arthritis, it will be necessary to treat it for a long time with small doses of cytostatics and corticosteroids.All this is used in combination with anti-inflammatory drugs.Modern treatment makes it possible to achieve long-term remission and reduce the use of hormonal medications to a minimum.





































